
Anthropology 391:B1, Hominid Evolution
Next in Winter 2015
MWF 11:00 to 11:50 am

Course description
This course is an examination of the operating world of the palaeoanthropologist in the 21st century. More and more genera and species of bipedal humans are being recognized (as of January 2007, there are 7 valid genera and 20 to 25 species), and researchers emphasize the anatomical diversity present over the last 5 to 6 million years. Living humans, Homo sapiens, are only a small remnant of a history of experiments in adaptation, most of which led to extinction.
After a brief general review, the first part of the course will deal with `human origins' taken literally. What evidence is there for the initial appearance of members of the Family Hominidae, in what contexts, and what conclusions have and can be drawn from it? How do palaeoanthropologists explain the origins of humans? This will include a detailed examination of the Miocene hominoid record, the origins of bipedalism, the first hominins, and then the australopithecines and early members of the genus Homo. Then the problem of the tempo and mode of evolution of the genus Homo will be examined, using Homo erectus as a focus. The last part of the course will deal with the current debate over the origins of anatomically modern humans (Homo sapiens). Fossil evidence, molecular data and other relevant sources of information will be examined for each period, along with models for causation and their behavioural implications. Prerequisite: Anthropology 209 or consent of the department.
Prerequisite: Anthropology 209 or consent of the department
Course requirements: Short written problem 20%; midterm exam 20%; term paper 30%; final exam 30%
Course outline for Winter 2013.
Text: Richard G. Klein (2009), The Human Career. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 3rd edition.
 Links
to related websites\
Links
to related websites\
American Anthropological Association website.
American Musuem of Natural History web site. The Anne and Bernard Spitzer Hall of Human Origins opened in 2007.
Archaeology Information. Information about archaeology, human evolution, human origins and hominin images.
American Association of Physical Anthropologists. Professional association; publishes American Journal of Physical Anthropology.
Becoming Human. Human evolution website sponsored by Donald Johanson and the Institute for Human Origins.
Becoming Human. A 3- part Nova (PBS) series on human evolution, aired first in November 2009.
eSkeletons. Everything you want to know about human osteology in one place. By John Kappelman at the University of Texas in Austin.
The Human Spark - a three part series about modern human origins on PBS in January 2010.
Fossil evidence for human evolution in 3D.
Paleoanthropology Society. For the study of human evolution.
Human origins and evolution in Africa. Dr. Jeanne Sept's website at Indiana University. Lots of good information about African prehistory, human evolution.
Center for Human Evolution Studies, Rutgers University.
Human Origins Program, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.
Institute for Human Origins. Located at Arizona State University.
Becoming Human. Human evolution website sponsored by Donald Johanson and the Institute for Human Origins.
Leverhulme Centre for Human Evolutionary Studies, Cambridge University.
All about human evolution, on the Talk Origins site.
Interactive web site reviewing the skeleton of humans, baboons and gorillas.
Evolution. On line version of PBS series on the evolution of life broadcast on September 24-27, 2001. Program 6 in the Evolution series: The Mind's Big Bang. What happened to humans around 50,000 years ago?
Origins. PBS series about the origins of the earth and life. September, 2004.
Origins Net. "Three Million Years of Prehistoric Art, Religion and Symbol in Human Evolution".
Origins blog of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Darwin. Web site to go with the American Museum of Natural History's exhibition on Darwin and evolution, November 2005.
Darwin Online. The complete works of Charles Darwin, for the bicentennial of his birth (2009).
L. S. B. Leakey Foundation for research on human origins.
The Stone Age Institute at Indiana University.
Walking with cavemen. Website connected to BBC show on human evolution, broadcast in 2003. Also Nature - prehistoric life.
University of California at Berkeley Museum of Palaeontology. Good information on geological time scale, systematics and evolution, cladistics.
National Museums of Kenya homepage.
Information about the Nobel Conferences at Gustavus Adolphus College in Minnesota. Theme for 2003 was "The story of life" and featured speakers such as Tim White, Niles Eldredge and Phillip Currie.
Palaeos - "The trace of life on earth". History of life, geological time scale, position of continents at various points in the past, etc.
 Dating
methods
Dating
methods
Berkeley Geochronology Centre. Information on dating methods for Palaeolithic and hominid sites.
Web site for Professor Jack Rink of McMaster University, a specialist in dating Middle and Upper Pleistocene sites.
Radiocarbon dating information.
Radiocarbon. Journal reporting radiocarbon dating results.
C-14 activity and global carbon cycle changes over the past 50,000 years, by K. Hughen et al. New article in Science 303(5655): 202-206; January 9, 2004.
Magnetic storm. PBS show on changes in the earth's magnetic field. Reviews palaeomagnetism and the evidence that another magnetic polarity reversal is due to take place.
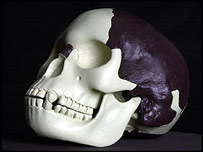 Piltdown
- the earliest Englishman? Not.
Piltdown
- the earliest Englishman? Not.
Charles Dawson: 'The Piltdown faker'. BBC News, November 21, 2003.
The boldest hoax. Nova (PBS), broadcast January 11, 2005.
Information about sites or fossil taxa (in roughly chronological order)
 (1)
Fossil non-human primates and people who study them
(1)
Fossil non-human primates and people who study them
Grasping primate origins by J. L. Bloch and D. M. Boyer. Science 298(5598): 1606-1610, November 22, 2002. (about Carpolestes simpsoni and the origin of true primates or Euprimates). Also commentary by E. J. Sargis.
David Begun's web site at the University of Toronto. David Begun does research on Miocene apes in Europe.
Planet of the apes by David Begun. Scientific American, August 2003.
Pierolapithecus catalaunicus, a new Middle Miocene great ape from Spain. Science 306(5700): 1339-1345, November 19, 2004. Also news item by E. Culotta.
New fossils raise molecular questions by Ann Gibbons, Science 295(5558): 1214-1219, Feb. 15, 2002.
Palaeontology - the road to Thailand. News item with link to Nature article concerning Lufengpithecus chiangmuanensis, a Middle Miocene ape, and orangutan origins. Nature, March 6, 2003.
Orang-utans: Family trees. News item with link to Nature article on Khoratpithecus piriyai, a Late Miocene ape related to orangutans; Nature, January 29, 2004.
 (2)
Sahelanthropus tchadensis. Chad hominin, 6 to 7 Mya
(2)
Sahelanthropus tchadensis. Chad hominin, 6 to 7 Mya
Toumai, the face of the deep. Nature news item, with links to the articles defining this species; also links to classic papers in human evolution published in past issues of Nature.
A fossil unearthed in Africa pushes back human origins. New York Times, July 12, 2002.
Sahelanthropus tchadensis, CNN article about new hominid from Chad, 6-7 million years old, July 10, 2002.
Father of us all. Time magazine, July 22, 2002.
Skulls found in Africa and in Europe challenge theories of human origins. New York Times, August 6, 2002.
The discovery of the Toumai skull.
Scientists clash over skull. BBC, October 9, 2002.
One scientist's quest for the origin of our species. Biography of Michel Brunet by Ann Gibbons. Science 298(5599): 1708-1710, November 29, 2002.
"Toumai - the human ancestor". Centre National de Recherche Scientifique (France) website on the Toumai discovery.
Facelift seals standing of oldest hominid. News@Nature article by J. Ebert, April 6, 2005.
 (3)
Ardipithecus ramidus and Ardipithecus kaddaba, Middle Awash,
Ethiopia
(3)
Ardipithecus ramidus and Ardipithecus kaddaba, Middle Awash,
Ethiopia
Website for the Human Evolution Research Center at the University of California, Berkeley. With interactive timeline for the Middle Awash research project.
Special issue of Science (October 2, 2009) on Ardipithecus ramidus. Video from Science (December 18, 2009) celebrating the year's top story.
Y. Haile-Selassie et al. "Late Miocene teeth from Middle Awash, Ethiopia and early hominid dental evolution". Science 303(5663): 1503-1505. With commentary by David Begun, "The earliest hominins: is less more?" Science 303(5663): 1478-1480 (2004).
Early pre-human lacked sharp canines. BBC News story about Ardipithecus kadabba, March 8, 2004.
Amazing hominid haul in Ethiopia. BBC News story about new specimens of Ardiputhecus ramidus from As Duma, Middle Awash, Ethiopia, January 19, 2005.
 (4)
Orrorin tugenensis, Lake Baringo, Kenya
(4)
Orrorin tugenensis, Lake Baringo, Kenya
Search for the first human. PBS show about Orrorin tugenensis broadcast May 8, 2002 as part of series "Secrets of the Dead".
In search of the first hominids by Ann Gibbons, Science 295(5558): 1214-1219, Feb. 15, 2002.
External and internal morphology of the BAR 1002'00 Orrorin tugenensis femur, by K. Galik et al.., Science 305(5689): 1450-1453, September 3, 2004.
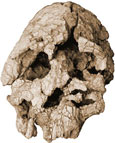 (5)
Kenyanthropus platyops (West Turkana)
(5)
Kenyanthropus platyops (West Turkana)
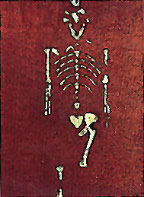 (6)
Australopithecus afarensis (Hadar, Ethiopia)
(6)
Australopithecus afarensis (Hadar, Ethiopia)
Institute for Human Origins. Located at Arizona State University.
Becoming Human. Human evolution website sponsored by Donald Johanson and the Institute for Human Origins.
(7) Australopithecus bahrelghazali
 (8)
Plio-Pleistocene hominids and their context
(8)
Plio-Pleistocene hominids and their context
Australopithecus garhi: a new species of early hominid from Ethiopia. B. Asfaw et al., Science 284(5414): 629-635, April 23, 1999.
Environment and behavior of 2.5 million year old hominids at Bouri, Ethiopia. J. de Heinzelin et al., Science 284(5414): 625-629, April 23, 1999.
Australopithecus sediba - a new hominin from South Africa. A link to a number of articles in difference issues of Science.
New clue on which came first, tools or better diets. By John Noble Wilford, New York Times, Octobe 21, 2003. Report about early stone tools from Ethiopia.
Paleolithic technology and human evolution. Review article by Stan Ambrose. Science 291(5509): 1748-1753, March 2, 2001.
Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site, South Africa.
Fossil find stirs human debate. BBC, January 31, 2003. About the skeleton from Member 2, Sterkfontein.
William Calvin's web site. Deals with his ideas on Quaternary climate change, human evolution, evolution of the brain and intelligence.
Killer cats hunted human ancestors. National Geographic news.
Encore Olduvai. P. Tobias. Science 299(5610): 1193-1194, February 28, 2003.
Late Pliocene Homo and hominid land use from Western Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania. R. Blumenschine et al. Science 299(5610): 1217-1220, February 28, 2003.
Cooking and how it slew the beast within. New York Times.
Bones hint at first use of fire. About Swartkrans, South Africa. BBC News, March 22, 2004
Jaw dropping theory of human evolution. Nature Science Update, March 24, 2004.
Distance running 'shaped human evolution' by M. Hopkin. Discussion of Nature article by D. Bramble and D. Lieberman about the origins of bipedalism, November 17, 2004.
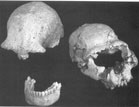 (9)
Homo erectus/ergaster and Out of Africa 1: the peopling of Eurasia
(9)
Homo erectus/ergaster and Out of Africa 1: the peopling of Eurasia
Were "little people" the first to venture out of Africa?. By M. Balter and A. Gibbons. Science, July 5, 2002.
A new skull of early Homo from Dmanisi, Georgia. A. Vekua et al. Science, July 5, 2002.
Skulls found in Africa and in Europe challenge theories of human origins. New York Times, August 6, 2002.
Pictures and description of new hominid from Dmanisi, Georgia. National Geographic, linked to August 2002 issue.
Stranger in a new land. Scientific American, November 2003. About Dmanisi.
Homo erectus calvarium from the Pleistocene in Java, by H. Baba et al. Science 299(5611): 1384-1389, February 28, 2003.
Peter Brown's Australian and Asian palaeoanthropology page. Australian and East Asian hominid pictures and descriptions.
 (10)
Homo heidelbergensis/ "archaic" Homo sapiens
(10)
Homo heidelbergensis/ "archaic" Homo sapiens
Sierra de Atapuerca. One of the most important early sites in Europe. This Spanish site has a number of localities including (a) the Gran Dolina, estimated to be around 800,000 years old, and (b) the Sima de los Huesos or "Pit of bones" which is between 200,000 and 300,000 years old. Together they have yielded a phenomenal number of hominid remains.
Disaster may have killed ancients. About the Sima de los Huesos people. BBC News, May 18, 2004.
Earliest human footprints found? In volcanic deposits in Italy, 385,000-325,000 years old. From Nature, March 13, 2003.
Ancient human occupation of Britain project.
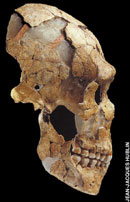 (11)
Neanderthals
(11)
Neanderthals
The Neanderthal Museum in Germany.
The Neanderthal Tools. Virtual Neanderthal site.
Neanderthals on trial. Broadcast on Nova, January 22, 2002.
Late Neanderthals were 'more like us'. About Vindija Cave, Croatia. BBC, January 2004.
Discovery of Middle Palaeolithic artifacts and mammoth bones in Munford, eastern England. From the CBC. More details available at the English Heritage web site.
Ancient human occupation of Britain project.
New work at the original Neandertal site in Germany: "Found bones complete Neanderthal 'family'". From CNN.
A rebuilt Neanderthal. About the American Museum of Natural History neandertal reconstruction. New York Times, December 31, 2002.
Whither the Neandertals? by Richard Klein. Science 299(5612): 1525-1527, March 7, 2003.
Study - neanderthals, humans didn't mix. CNN, March 7, 2003.
Did humans and Neandertals battle for control of the Mid East? National Geographic News, March 8, 2002.
Study - that Neanderthal was not your grandfather. CNN.com, January 27, 2004.
Early man steered clear of Neanderthal romance. Nature Science Update, March 15, 2004. With link to article by D. Serre et al., PLos Biology, (March 2004) examining Neandertal and early modern human mitochondrial DNA.
Neanderthal DNA Web Focus, Special on-line information from Nature, November 16, 2006. Marking publication for first paper on the Neanderthal nuclear genome.
Special Feature: The Neandertal genome. Science, May 6, 2010.
Decoding Neanderthals - a NOVA show, aired on PBS on January 8, 2012.
 (12)
Modern Homo sapiens
(12)
Modern Homo sapiens
Christopher Stringer re-envisions human origins. Online article from The Edge (December 11, 2011).
Lascaux, a French Upper Palaeolithic rock art site. Also with links to other French cave art sites.
Jawbone hints at earliest Britons by Paul Rincon. BBC, Aptil 27, 2005.
Fossil findings blur picture of art's birth. Nature news story about redating the modern humans of Vogelherd, Germany, July 4, 2004.
Origins. News story from Harvard alumni magazine about Ofer Bar-Yosef's research on modern human origins as well as Neolithic origins in the Middle East.
Dan Lieberman's web site at Harvard University. Lieberman studies brain evolution in the genus Homo and modern human origins.
CAT scans of Skhul V, an early modern human from Mt. Carmel, Israel. Presented by Dan Lieberman, Harvard University.
Pamela Willoughby's book on The Evolution of Modern Humans in Africa: A Comprehensive Guide. Lanham, Maryland: AltaMira Press, 2007, 439 pp.
Ethiopia is top choice for cradle of Homo sapiens. News at Nature article about new dates for Omo Kibish by M. Hopkin; February 17, 2005.
Website for the Human Evolution Research Center at the University of California, Berkeley. With interactive timeline for the Middle Awash research project.
Age of ancient humans reassessed. Re Omo-Kibish. BBC News, February 17, 2005.
African origins: Ethiopian fossils are the earliest Homo sapiens. Links to Nature articles published June 12, 2003.
Fossil skulls offer first glimpse of early human faces by John Noble Wilford, New York Times, June 11, 2003.
In ancient skulls from Ethiopia, familiar faces by John Noble Wilford, New York Times, June 12, 2003.
Mungo man versus mitochondrial Eve. Discovery Channel Canada story about DNA extraction from Mungo 3, an early Australian.
Dating of Australian remains backs theory of early migrations of humans. Nicholas Wade, New York Times, February 19, 2003.
The human colonization of Australia: dating early occupation sites at Lake Mungo by J. M. Bowler et al. Nature, February 20, 2003.
The strange new hominid from Flores, Indonesia. Link to a series of articles in Nature, October 27, 2004.
The faculty of language: what is it, who has it and how did it evolve? By M. Hauser, N. Chomsky and T. Fitch. Science 298(5598): 1569-1579, November 22, 2002. With commentary by T. Bever and M. Montalbetti.
First words. E. Culotta and B. Hanson. The introduction to a special issue of Science on the evolution of language, February 27, 2004.
We are all Africans. Pat Shipman discusses the latest information about modern human origins in this article from American Scientist, November-December 2003.
Program 6 in the Evolution series: The Mind's Big Bang. What happened to humans around 50,000 years ago?
America's Stone Age explorers. Nova (PBS) show on peopling the Americas, November 2004.
 Dating
methods
Dating
methods
New dating techniques discussed.
Berkeley Geochronology Centre. Information on dating methods for early hominid sites.
Web site for Professor Jack Rink of McMaster University, a specialist in dating Middle and Upper Pleistocene sites.
Radiocarbon dating information.
 General
science journals, which publish occasional articles on primate and human evolution
General
science journals, which publish occasional articles on primate and human evolution
American Scientist. Journal of Sigma Xi, the Scientific Research Society, bi-monthly.
Nature. British science journal (weekly); also has link to the journal Nature Genetics (monthly).
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Biweekly.
Science. American science journal. Weekly.
Scientific American. Monthly.
 Other
journals or sources on human evolution and its context
Other
journals or sources on human evolution and its context
Current Anthropology. Articles with CA comment by other specialists. Many papers on modern human cultural origins.
Evolutionary Anthropology. Good general articles on all aspects of human evolution.
Geoarchaeology. Articles on palaeoenvironments, geology and archaeology.
Journal of Anthropological Research. Articles on all aspects of anthropology, occasional ones on palaeoanthropology. Edited by Lawrence Straus, a Palaeolithic archaeologist.
Journal of Archaeological Science. Archaeometry papers. Available from Science Direct through the University of Alberta e-journals list
Journal of Human Evolution. Articles on all aspects of human evolution. Available from Science Direct through the University of Alberta e-journals list
Paleobiology. Palaeontology journal, with a focus on macroevolution, punctuated equilibria. Find through University of Alberta e-journals list.
 Quaternary
environments and human evolution
Quaternary
environments and human evolution
Cracking the ice age. PBS Nova.
Cycles, cycles everywhere. Review of evidence for Milankovitch glacial cycling. Enhanced web site by T. J. Crowley published in Science 295(5559): 1473-1474, February 22, 2002.
EPICA adventure. Nature stories about the EPICA (European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica) 740,000+ year ice core, June 10, 2004.
Quaternary refugia and persistence of biodiversity. Enhanced website by P. Taberlet and R. Cheddadi, published by Science, September 20, 2002.
International Geosphere-Biosphere Core project on past global changes (PAGES).
International Quaternary Association (INQUA).
Journal of Quaternary Science.
Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. Past environmental information, from all periods, including the Quaternary.
Quaternary Environment Network. Information on environments of last 2 million years. Each continent is illustrated with maps from key periods; lots of documentation about evidence for palaeoenvironmental reconstruction.
Quaternary International. Each issue on a separate topic. January 2001: "Out of Africa in the Pleistocene".
Quaternary Research. Palaeoenvironments, palaeontology and archaeology of last 2 million years. Available from Science Direct through the University of Alberta e-journals list.
Quaternary Research Association.
Quaternary Science Reviews. Research papers on Quaternary environments, geology and archaeology.
QUEEN. Quaternary Environments of the Eurasian North.
Intergovernmental panel on climate change. Modern evidence for climatic change and what it may tell us about the past.
C-14 activity and global carbon cycle changes over the past 50,000 years, by K. Hughen et al. New article in Science 303(5655): 202-206; January 9, 2004.
Ice core reveals gentle start to last Ice Age. By M. Peplow. News@Nature.com, September 8, 2004.
 Genetics
and hominoid evolution
Genetics
and hominoid evolution
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Major genetic research centre; has hosted 4 conferences on human origins betwen 1997 and 2002.
Genetic origins. Cold Spring Harbor web site about genetics and human evolution.
Cracking the code of life. PBS Nova.
DNA from the beginning. Introduction to evolutionary genetics, created by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Double helix: 50 years of DNA. News articles from Nature celebrating the 50th anniversay of the discovery of the structure of DNA, January 23, 2003.
A revolution at 50. Special anniversary series on the discovery of the structure of DNA, New York Times, February 25, 2003.
DNA at 50. BBC site celebrating the 50th anniversary of the discovery of the structure of DNA (2003).
Max Planck Instutute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Leipzig, Germany. Centre for research on human biology and evolution, especially modern or ancient human DNA work of Svante Paabo, Mark Stoneking and colleagues.
Chimpanzee chromosome creates puzzles. Nature Science Update article about chimpanzee chromosome 22 research. May 27, 2004.
The chimpanzee genome. Introduction and editorial summary for series of papers published in Nature on September 1, 2005.
"Journey" redraws humans family tree. About Spencer Wells' research on human DNA, the Genographic Project and his book Journey of Man.
Journal of Molecular Evolution. Occasionally has papers on primate and human evolutionary genetics.
ALFRED = Allele Frequency Database. From Ken Kidd's lab at Yale University.
mtDB. Human Mitochondrial Genome database. Has completed mtDNA sequences, software for analysis.
Mitomap: Human mitochondrial genome database.
The Human Genome. Special "web focus" site produced by Nature in 2003.
The International HapMap Consortium. For information on single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs.
HapMap: mapping all over the world. About the International HapMap Project, designed to measure the genetic diversity in humans worldwide. Nature, December 18, 2003.
The Y chromosome. Special feature in Nature (June 19, 2003) on sequencing the male sex chromosome.
Tangled roots? Genetics meets geneology by K. Brown, Science 295(5560): 1634-1635, March 1, 2002.
Language gene is traced to emergence of humans. New York Times, August 15, 2002.
Gene 'helped create human brain'. BBC News, January 14, 2004.
Oxford Ancestors. "Putting the genes in geneology" Bryan Syke's web site where, regardless of your ethnicity, they can trace your mitochondrial and Y-chromosome ancestry.
Stomachs out of Africa, by B. G. Spratt. Science 299(5612): 1528-1529, Comment on article, by D. Falush, et al., Traces of human migrations in Helicobactor pylori populations, Science 299(5612): 1582-1585, March 8, 2003.
Ancient DNA mutations permitted humans to adapt to colder climates, researchers find. Science Daily, January 14, 2004.
Human migration tracked in Stanford computer simulation. Science Daily, January 22, 2004.
The poop on ancient man. Globe and Mail story about Hendrik Poinar, McMaster University, and his search for DNA via feces, June 19, 2004.
Did early humans go north or south? Enhanced article on mitochondrial DNA of Asia and Out of Africa 2. Science, May 13, 2005.
Neanderthal DNA Web Focus, Special on-line information from Nature, November 16, 2006. Marking publication for first paper on the Neanderthal nuclear genome.
Special Feature: The Neandertal genome. Science, May 6, 2010.
 Palaeoanthropological
field schools for 2013
Palaeoanthropological
field schools for 2013
The Koobi Fora field school offered in northern Kenya by Rutgers University.
Field school in Paleoanthropology and Palaeolithic archaeology in Serbia offered by the University of Winnipeg.
![]() And
last but not least!
And
last but not least!
Is human evolution finally over? From Robin McKie of the Observer.
The National Center for Science Education. Still the best place for information on the struggle between evolution and creationism. Its director, Eugenie Scott, has a nice article on Antievolutionism and creationism in the US in the Annual Review of Anthropology 26: 263-289, 1997.
The crusade against evolution by Evan Ratliff. Wired Magazine, October 2004.
The Darwin Awards. Given annually to those who remove themselves from the gene pool in ever creative and novel ways. See human evolution in action! Lots more evolution information too. Or as they say, "Don't leave the trees without it!".

Go to top.
Click here to go to Pam Willoughby's home page.