 Anthropology
313:B1, Middle and Upper Palaeolithic Prehistory
Anthropology
313:B1, Middle and Upper Palaeolithic Prehistory Anthropology
313:B1, Middle and Upper Palaeolithic Prehistory
Anthropology
313:B1, Middle and Upper Palaeolithic Prehistory
Next in Winter 2016


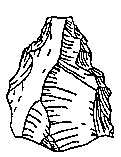
(a) Gravettian tools from La Ferrassie, France. (b) Lions from Chauvet Cave, France.
Course description
7This course reviews what we know about the behaviour and evolution of later Pleistocene humans in the Old World through their material culture and technology. It begins with the transition from the Lower Palaeolithic and the initiation of regional variation in stone tool assemblages around 200,000 years ago and ends with the cultural changes which took place in response to deglaciation around 10,000 years ago. The earlier period is labelled the Middle Palaeolithic, and its flake tool dominated assemblages are associated with archaic Homo sapiens (including the Neandertals) or anatomically modern humans. These assemblages are replaced around 30-40,000 years ago by blade tool industries belonging to the Upper Palaeolithic, always found in association with modern humans. This course will examine the archaeological evidence for the Middle and Upper Palaeolithic in Europe, Asia and Africa, and what it contributes to the understanding of recent human evolution. The problem of the initial occupation of Australia and New Guinea will also be examined.
Prerequisite: Anthropology 206 or consent of department.
The Course outline from a previous year is available here.
Course Requirements: Mid-term exam 20%; 2 critical summaries 20%; term paper 30%; final exam 30%.
Text: There is no required trextbook. A list of required readings is available on the E-class site.
 Related
websites
Related
websites
American Anthropological Association website.
American Museum of Natural History web site. Also link to their magazine, Natural History. The Anne and Bernard Spitzer Hall of Human Origins opened in 2007.
Archaeology Information. Information about archaeology, human evolution, human origins and hominid images.
Becoming Human. Human evolution website sponsored by Donald Johanson and the Institute for Human Origins.
Becoming Human. A 3- part Nova (PBS) series on human evolution, aired first in November 2009.
Center for Human Evolution Studies, Rutgers University.
Evolution. On line version of PBS series on the evolution of life broadcast on September 24-27, 2001. Program 6 in the Evolution series: The Mind's Big Bang. What happened to humans around 50,000 years ago?
Human Origins Program, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.
The Human Spark - a three part series about modern human origins on PBS in January 2010.
Institute for Human Origins. Located at Arizona State University.
Origins. PBS series about the origins of the earth and life. First shown in September 2004.
Origins Net. "Three Million Years of Prehistoric Art, Religion and Symbol in Human Evolution".
Darwin. Web site to go with the American Museum of Natural History's exhibition on Darwin and evolution, November 2005.
L. S. B. Leakey Foundation for research on human origins.
Paleoanthropology Society. For information on all aspects of human evolution.
University of California at Berkeley Museum of Palaeontology. Good information on geological time scale, systematics and evolution.
Website for the Human Evolution Research Center at the University of California, Berkeley. With interactive timeline for the Middle Awash research project.
Palaeos - "The trace of life on earth". History of life, geological time scale, position of continents at various points in the past, etc.
Walking with cavemen. Website connected to BBC show on human evolution, broadcast in 2003. Also Walking with beasts (about Cenozoic mammal evolution).
 Middle
and Upper Palaeolithic news
Middle
and Upper Palaeolithic news
Christopher Stringer re-envisions human origins. Online article from The Edge(December 11, 2011).
Paleolithic technology and human evolution. Review article by Stan Ambrose. Science 291(5509): 1748-1753, March 2, 2001.
Is the evidence for human "replacement" really clear? From Geoffrey Clark and Lawrence Straus.
Debate is fueled on when humans became human. From the New York Times.
What made humans modern? by M. Balter, Science 295(5558): 1219-1225, February 15, 2002.
Why get smart? by M. Balter, Science 295(5558): 1225, February 15, 2002.
First words. E. Culotta and B. Hanson. The introduction to a special issue of Science on the evolution of language, February 27, 2004.
Language gene is traced to emergence of humans. New York Times, August 15, 2002.
Faces from the ice age. BBC.
Neanderthal DNA Web Focus, Special on-line information from Nature, November 16, 2006. Marking publication for first paper on the Neanderthal nuclear genome.
 Eurasia
Eurasia
The Neanderthal Museum in Germany.
Neanderthals on trial. Broadcast on Nova, January 22, 2002.
Study - that Neanderthal was not your grandfather. CNN.com, January 27, 2004.
Old Stone Age website. For study of the Palaeolithic. Research done by Harold Dibble and Shannon MacPherron.
Ancient human occupation of Britain project.
Special Feature: The Neandertal genome. Science, May 6, 2010.
Decoding Neanderthals - a NOVA show, aired on PBS on January 8, 2012.
Jawbone hints at earliest Britons by Paul Rincon. BBC, April 27, 2005.
Les Eyzies, the world capital of prehistory. Official touist web site.
Musee national de préhistoire, Les Eyzies de Tayac, France.
Cussac. New French Palaeolithic art site, with human burials.
Chauvet Cave. French Upper Palaeolithic rock art site, possibly oldest in Europe.
Lascaux, a French Upper Palaeolithic rock art site. Also with links to other French cave art sites.
Cosquer Cave. French Upper Palaeolithic rock art site near Marseilles. Unique in that entrance is now submerged and site is only accessible by scuba divers.
Oldest sculptures unearthed. About Hohle Fels, Germany figurines, Nature, December 18, 2003.
Fossil findings blur picture of art's birth. Nature news story about redating the modern humans of Vogelherd, Germany, July 4, 2004.
Humans sped to UK after the ice age. What happens towards the end of the Pleistocene? National Geographic News, November 3, 2003.
Excavations in Eastern Europe reveal ancient human lifestyles. About Kostenki, Ukraine. From Eureka Alert.
Did humans and neandertals battle for control of the Mid East? National Geographic News, March 8, 2002.
Ucagizli Cave project web site.
Humans lived in ice age Tibet 20,000 years ago. From Science Update.
Origins. News story from Harvard alumni magazine about Ofer Bar-Yosef's research on modern human origins as well as Neolithic origins in the Middle East.
 Africa
Africa
Human origins and evolution in Africa. Dr. Jeanne Sept's website at Indiana University. Lots of good information about African prehistory, human evolution.
Ethiopia is top choice for cradle of Homo sapiens. News at Nature article about new dates for Omo Kibish by M. Hopkin; February 17, 2005.
Age of ancient humans reassessed. Re Omo-Kibish. BBC News, February 17, 2005.
African origins: Ethiopian fossils are the earliest Homo sapiens. Links to Nature articles published June 12, 2003.
Fossil skulls offer first glimpse of early human faces by John Noble Wilford, New York Times, June 11, 2003.
In ancient skulls from Ethiopia, familiar faces by John Noble Wilford, New York Times, June 12, 2003.
Koobi Fora field school. Offered annually by Rutgers University. East of Lake Turkana, northern Kenya. Source of many important Lower Palaeolithic archaeological sites and early hominids.
National Museums of Kenya homepage.
Blombos Cave field school. Offered by State University of New York at Stony Brook annually starting in February 2002. Excavations at Blombos Cave, South Africa, an extremely important Middle Stone Age (MSA) site near Cape Town.
Humans fully modern earlier than thought. From The Discovery Channel. About ochre carving at Blombos Cave, South Africa, during the MSA.
Information about finds at Blombos Cave, a South African MSA site, and the beginnings of cultural modernity.
Cave yields earliest jewelry. BBC News, April 15, 2004.
Emergence of modern human behavior: MSA engravings from South Africa by C. Henshilwood et al. Science 295(5558): 1278-1280, February 15, 2002.
Sibudu Cave field school. Offered by the University of Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa. Excavation at this important Middle Stone Age (MSA) site.
Pam Willoughby's research page (The stone age prehistory of southwestern Tanzania).
Southeast Asia and Australia
Australasian Centre for human evolution.
Peter Brown's Australian and Asian palaeoanthropology page. Australian and East Asian hominid pictures and descriptions.
Mungo man versus mitochondrial Eve. Discovery Channel Canada story about DNA extraction from Mungo 3, an early Australian.
Dating of Australian remains backs theory of early migrations of humans. Nicholas Wade, New York Times, February 19, 2003.
The human colonization of Australia: dating early occupation sites at Lake Mungo by J. M. Bowler et al. Nature, February 20, 2003.
The strange new hominid from Flores, Indonesia. Link to a series of articles in Nature, October 27, 2004.
 Dating
techniques
Dating
techniques
Berkeley Geochronology Centre. Information on dating methods for Palaeolithic and hominid sites.
New dating techniques discussed.
Web sites for Professors Henry Schwarz and Jack Rink of McMaster University. Both are specialists in dating Middle and Upper Pleistocene sites.
Radiocarbon dating information.
Radiocarbon. Journal reporting radiocarbon dating results.
C-14 activity and global carbon cycle changes over the past 50,000 years, by K. Hughen et al. New article in Science 303(5655): 202-206; January 9, 2004.
 Quaternary
environments and human prehistory
Quaternary
environments and human prehistory
Cracking the ice age. PBS Nova.
Cycles, cycles everywhere. Review of evidence for Milankovitch glacial cycling by T. J. Crowley. Enhanced web site from Science 295(5559): 1473-1474, February 22, 2002.
EPICA adventure. Nature stories about the EPICA (European Poroject for Ice Coring in Antarctica) 740,000+ year ice core, June 10, 2004.
Quaternary refugia and persistence of biodiversity. Enhanced website by P. Taberlet and R. Cheddadi, published by Science, September 20, 2002.
Oxygen isotope stage 3 research group. What was going on environmentally when neandertals and modern humans met in Europe?
Big chill killed off the neanderthals. What was going on in Europe during OIS 3 anyway? New Scientist, January 21, 2004.
University of California at Berkeley Museum of Palaeontology. Good information on geological time scale, systematics and evolution, cladistics.
Global and Planetary Change. Journal with palaeoenvironmental data.
International Quaternary Association (INQUA).
INQUA Commission on Human Evolution and Paleoecology.
Journal of Quaternary Science.
International Geosphere-Biosphere Core project on past global changes (PAGES).
Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. Past environmental information, from all periods, including the Quaternary.
Quaternary Environment Network. Information on environments of last 2 million years. Each continent is illustrated with maps from key periods; lots of documentation about evidence for palaeoenvironmental reconstruction.
Quaternary International. Each issue on a separate topic. January 2001: "Out of Africa in the Pleistocene".
Quaternary Research. Palaeoenvironments, palaeontology and archaeology of last 2 million years. Available from Science Direct through the University of Alberta e-journals list. Volume 58(1) published in July 2002 is a special issue "Eemfest" on the last interglacial or Eem (in Europe).
Quaternary Research Association.
Quaternary Science Reviews. Research papers on Quaternary environments, geology and archaeology.
QUEEN. Quaternary Environments of the Eurasian North.
World Data Center for Paleoclimatology.
Intergovernmental panel on climate change. Modern evidence for climatic change and what it may tell us about the past.
What drove past teleconnections. by Frank Sirocko. Science 301(5638): 1336-1337; September 5, 2003.
Indian Ocean climate and an absolute chronology over Dansgaard/Oeschger events 9 to 13. By S. J. Burns et al. Science 301(5638): 1365-1367; September 5, 2003.
Ice core reveals gentle start to last Ice Age. By M. Peplow. News@Nature.com, September 8, 2004.
 General
science journals, which publish occasional articles on human biological or cultural
evolution
General
science journals, which publish occasional articles on human biological or cultural
evolution
American Scientist. Journal of Sigma Xi, the Scientific Research Society.
Nature. British science journal; also has link to the journal Nature Genetics.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Science. Produced by the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
 Journals
with articles on human evolution and/or the Palaeolithic
Journals
with articles on human evolution and/or the Palaeolithic
African Archaeological Review. Papers on African prehistory. Find through University of Alberta e-journals list.
American Antiquity. New World prehistory, but occasionally articles on Palaeolithic subjects.
Antiquity. British general archaeological journal; world coverage.
Archaeology. Popular archaeology magazine; published by Archaeological Institute of America.
Cambridge Archaeological Journal. Follow links to journal. Many papers on the beginnings of symbolic behaviour and the Middle/Upper Palaeolithic transition.
Current Anthropology. Articles with CA comment by other specialists. Many papers on modern human cultural origins.
Evolutionary Anthropology. Good general articles on all aspects of human evolution.
Geoarchaeology. Articles on palaeoenvironments, geology and archaeology.
Journal of Anthropological Archaeology. Available from Science Direct through the University of Alberta e-journals list
Journal of Anthropological Research. Articles on all aspects of anthropology, occasional ones on palaeoanthropology. Edited by Lawrence Straus, a Palaeolithic archaeologist.
Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory.
Journal of Archaeological Science. Archaeometry papers. Available from Science Direct through the University of Alberta e-journals list
Journal of Human Evolution. Articles on all aspects of human evolution. Available from Science Direct through the University of Alberta e-journals list
Journal of World Prehistory. Review papers summarizing culture history for specific regions. Find through University of Alberta e-journals list.
Oxford Journal of Archaeology. Find through University of Alberta e-journals list.
World Archaeology. Each issue on a single theme. Find through University of Alberta e-journals list.

Go to top.
Click here to go back to Pam Willoughby's home page.